
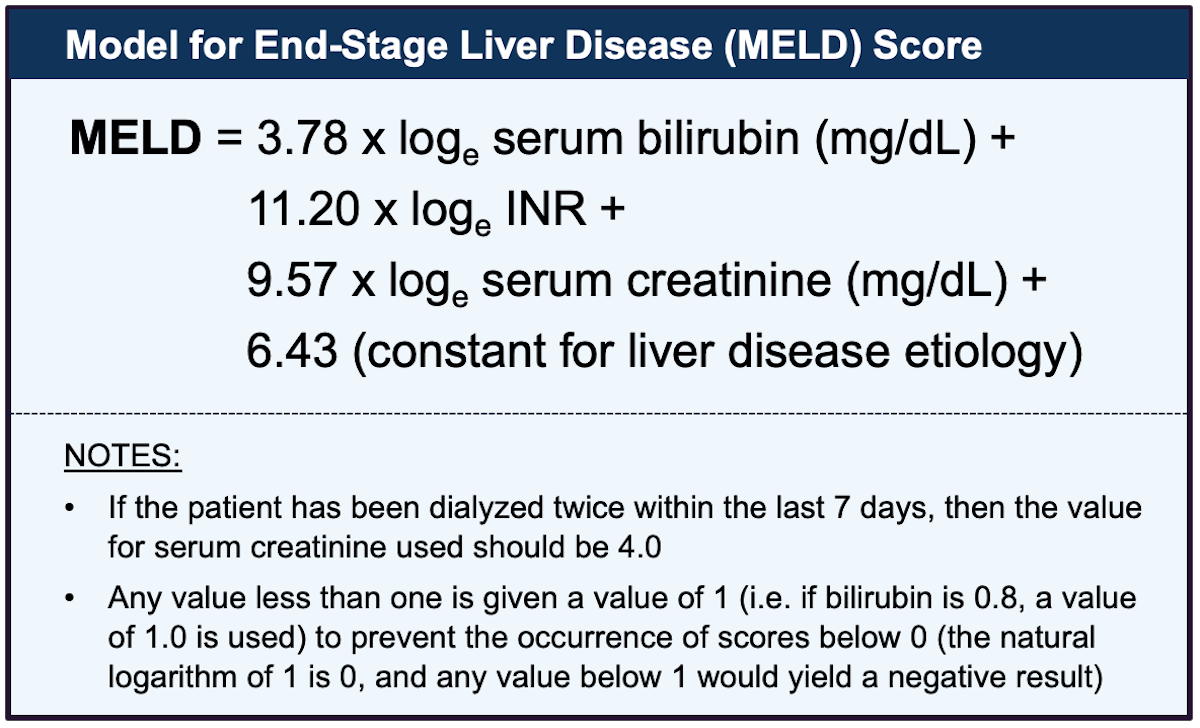
The study showed: (1) the MELD, the CTP score, and the Emory score were similar in accuracy for predicting three-month mortality (2) the MELD was more accurate than the others for predicting 12-month mortality and (3) the MELD and the CTP score were more accurate than the Emory score for predicting 36-month mortality. The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) calculator provides a ‘score’ (number) based on how urgently someone needs a liver transplant in the next three months. The accuracy of each score was measured using the concordance-statistic (c-statistic): 1 was a score that perfectly predicted the outcome in question, and 0 was a score that failed to predict any outcome correctly. The mean age of patients was 57 years, about two thirds were men, and most had alcoholic cirrhosis. 4 The study used the version of the MELD that included creatinine, bilirubin, INR, and cause of cirrhosis. These patients have the highest priority to receive an organ and are not affected by the MELD system.A German study compared the MELD, the CTP score, and the Emory score in predicting the prognosis of 162 patients with end-stage liver disease who were undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting (TIPS). This will help ensure that livers go to the sickest patient, that is the person in greatest need at that time.Ĭategory 1 and 2 patients have acute liver failure and a very short life expectancy without a transplant. MELD can fluctuate based on your current condition, with variations from a few points as lab values vary to a larger increase if you have an infection or an acute decompensation (worsening of your liver disease). MELD MELD (i) + 1.32 (137-Na) - 0.033MELD (i) (137-Na) Notes This version of the MELD calculator includes United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) modifications of the original model. The MELD score ranges from 6 to 40, and is a measure of how severe a patient’s liver disease is. Your MELD score will be assessed monthly whilst you are on the waiting list. MELD (i) round 1 0.378 log e (bilirubin)) + (1.120log e (INR)) + (0.957log e (creatinine)) + 0.643 10 1 rounded to the tenth decimal place. A patient’s MELD score may go up or down over time depending on the status of his or her liver disease. The majority of patients waiting for a liver transplantation have chronic liver disease and are listed as Category 3 and have their MELD score calculated regularly. It is calculated according to the following formula: MELD 3.78×lnserum bilirubin (mg/dL) + 11.2×lnINR + 9.57×lnserum creatinine (mg/dL) + 6. The calculation of MELD was performed using the formula. Poor kidney function is often associated with severe liver disease. The ROC curves for death identified the MELD score as the cutoff point. Creatinine, which measures kidney function.INR, prothrombin time, which measures the liver’s ability to make blood clotting factors and.Bilirubin, which measures how effectively the liver excretes bile.The number is calculated by a formula using 3 routine laboratory test results:
The MELD score is also used to identify patients who are too well and do not need a liver transplant. Research has shown that MELD accurately predicts most patient’s short-term risk ofĭeath without a liver transplant. It gives each patient a ‘score’ or number based on how urgent he or she needs a liver transplant in the next 3 months. MELD is a numerical scale, ranging from 6 which is less ill to 40 which is gravely ill. It is also important to have a good size match between the donor liver and you, the recipient. Patients waiting for liver transplantation need a donor with the same blood group as the recipient. It is based on a statistical formula that predicts which individuals are most likely to die from their liver disease. MELD is used to prioritise and allocate adult patients waiting for a liver transplant. Print Liver Transplant Evaluation and Assessment Guide Model for End stage Liver Disease (MELD) MELD Score (2016) MELD(i) + 1.32(137-Na) 0.033MELD(i)(137-Na) Where MELD(i) is the original MELD score without serum sodium.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
